| Developer(s) | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Initial release | July 1996; 25 years ago with the release of OPENSTEP 4.0[1] |
| Stable release | 1.16 / 12 November 2020; 10 months ago |
| Operating system | Originally released for NeXTSTEP, released for Mac OS X (now macOS) after Apple's purchase of NeXT; Ported to all GNUstep systems (up to 1.6) |
| Type | Text editor, word processor |
| License | BSD-3-Clause |
| Website | developer.apple.com/library/mac/samplecode/TextEdit |
You can use the tab stops on the ruler to align text. In the TextEdit app on your Mac, do any of the following. Add a tab stop: Click the ruler where you want the tab stop. Change the type of tab stop: Control-click a tab stop, then choose one of the following tab stops: Left tab: Left-aligns text. Center tab: Centers text. Right tab: Right-aligns text. All text editors should be able to open any text file, especially if there isn't any special formatting being used. For example, TXT files can be opened with the built-in Notepad program in Windows by right-clicking the file and choosing Edit. Similar for TextEdit on a Mac. Name Description License E: is the text editor in PC DOS 6, PC DOS 7 and PC DOS 2000. Proprietary: ed: The default line editor on Unix since the birth of Unix. Either ed or a compatible editor is available on all systems labeled as Unix (not by default on every one).
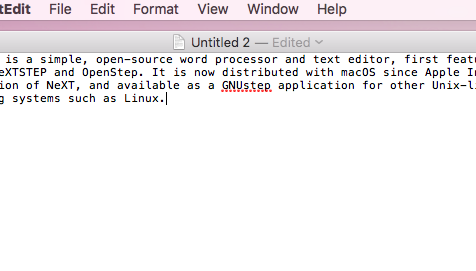
TextEdit is a simple, open-sourceword processor and text editor, first featured in NeXT's NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP. It is now distributed with macOS since Apple Inc.'s acquisition of NeXT, and available as a GNUstep application for other Unix-like operating systems such as Linux.[2] It is powered by Apple Advanced Typography and has many advanced typographic features.
Implementation[edit]
TextEdit replaced the text editor of previous Macintosh operating systems, SimpleText. TextEdit uses the Cocoa text system to read and write documents in Rich Text Format (RTF), Rich Text Format Directory, plain text, and HTML formats, and can open (but not save) old SimpleText files. It also has access to the operating system's built-in spell-checking service. The version included in Mac OS X v10.3 added the ability to read and write documents in Word format, and the version in Mac OS X v10.4 added the ability to read and write Word XML documents. The version included in Mac OS X v10.5 added read and write support for Office Open XML and OpenDocument Text. The version included in Mac OS X v10.6 added automatic spelling correction, support for data detectors, and text transformations. The version included in Mac OS X v10.7 added versioning of files, and Autosave similar to iOS.
Formatted text, justification, and even the inclusion of graphics and other multimedia elements are supported by TextEdit, as well as the ability to read and write to different character encodings, including Unicode (UTF-8 and UTF-16). TextEdit automatically adjusts letter spacing in addition to word spacing while justifying text. TextEdit does not support multiple columns of text.
The high-resolution TextEdit 1.5 icon found in Mac OS X versions starting with 10.5 (Leopard) features an extract from Apple's 'Think different' ad campaign. This was replaced by a blank sheet of notebook paper in 10.10 (Yosemite).
Source code[edit]
Apple formerly distributed TextEdit's source code as part of the documentation of its integrated development environment (IDE) Xcode. On the Internet, the source code of TextEdit can be found in Apple's Mac Developer Library.[3] The following quote is from the characteristic part of the BSD-3-Clause-compliant license text included in the source code:

[...] In consideration of your agreement to abide by the following terms, and subject to these terms, Apple grants you a personal, non-exclusive license, under Apple's copyrights in this original Apple software (the 'Apple Software'), to use, reproduce, modify and redistribute the Apple Software, with or without modifications, in source and/or binary forms; provided that if you redistribute the Apple Software in its entirety and without modifications, you must retain this notice and the following text and disclaimers in all such redistributions of the Apple Software. Neither the name, trademarks, service marks or logos of Apple Computer, Inc. may be used to endorse or promote products derived from the Apple Software without specific prior written permission from Apple. Except as expressly stated in this notice, no other rights or licenses, express or implied, are granted by Apple herein, including but not limited to any patent rights that may be infringed by your derivative works or by other works in which the Apple Software may be incorporated.[...]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'Logiciels NeXT (Fr)'. Retrieved March 25, 2019.
- ^'Backbone—A GNUstep based desktop environment'. Retrieved September 4, 2007.
- ^'About TextEdit'. Apple, Inc. August 26, 2013. Retrieved August 17, 2017.
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to TextEdit. |
- TextEdit in Mac Developer Library (with source code)
TextEdit User Guide
Textwrangler
You can use TextEdit to edit or display HTML documents as you’d see them in a browser (images may not appear), or in code-editing mode.
Note: By default, curly quotes and em dashes are substituted for straight quotes and hyphens when editing HTML as formatted text. (Code-editing mode uses straight quotes and hyphens.) To learn how to change this preference, see New Document options.
Text Editor Mac Free
Create an HTML file
In the TextEdit app on your Mac, choose File > New, then choose Format > Make Plain Text.
Enter the HTML code.
Choose File > Save, type a name followed by the extension .html (for example, enter index.html), then click Save.
When prompted about the extension to use, click “Use .html.”
View an HTML document
In the TextEdit app on your Mac, choose File > Open, then select the document.
Click Options at the bottom of the TextEdit dialog, then select “Ignore rich text commands.”
Click Open.
Always open HTML files in code-editing mode
In the TextEdit app on your Mac, choose TextEdit > Preferences, then click Open and Save.
Select “Display HTML files as HTML code instead of formatted text.”
Change how HTML files are saved
Set preferences that affect how HTML files are saved in TextEdit.
In the TextEdit app on your Mac, choose TextEdit > Preferences, then click Open and Save.
Below HTML Saving Options, choose a document type, a style setting for CSS, and an encoding.
Select “Preserve white space” to include code that preserves blank areas in documents.
If you open an HTML file and don’t see the code, TextEdit is displaying the file the same way a browser would (as formatted text).